Steps to Create an Executable from Python Script using PyInstaller
Step 1: Install Python and Add Python to Windows Path
An easy way to add Python to the path is by downloading a recent version of Python and then checking the box to ‘Add Python to PATH’ at the beginning of the installation.
For detailed steps of Python installation please check this tutorial.
Step 2: Open the Windows Command Prompt
Next, open the Windows Command Prompt. Press Win+R and type “cmd” and then press Enter.
Step 3: Install the Pyinstaller Package
In the Windows Command Prompt, type the following command to install the pyinstaller package (and then press Enter):
pip install pyinstaller
Step 4: Save your Python Script
Now you’ll need to save your Python script at your desired location.
For illustration purposes, I created a simple Python script that will display ‘Hello World!’ when clicking the button:
import tkinter as tk
root= tk.Tk()
canvas1 = tk.Canvas(root, width = 300, height = 300)
canvas1.pack()
def hello ():
label1 = tk.Label(root, text= 'Hello World!', fg='green', font=('helvetica', 12, 'bold'))
canvas1.create_window(150, 200, window=label1)
button1 = tk.Button(text='Click Me',command=hello, bg='brown',fg='white')
canvas1.create_window(150, 150, window=button1)
root.mainloop()
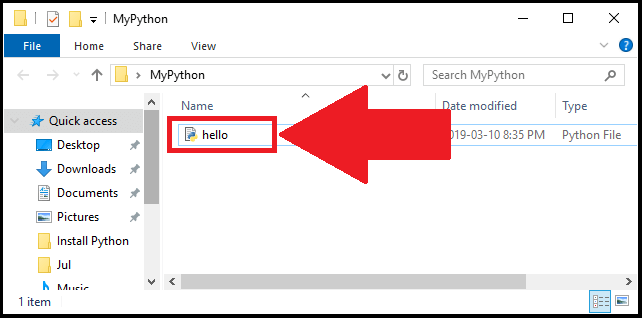
I then saved the Python script in the following folder:
C:\Users\myTechMint\Desktop\MyPython
Where I named the Python script as ‘hello’
Step 5: Create the Executable using Pyinstaller
Now you’ll be able to create the executable from the Python script using PyInstaller.
Simply go to the Command Prompt, and then type:
cd followed by the location where your Python script is stored
In my case, I typed the following in the command prompt:
cd C:\Users\myTechMint\Desktop\MyPython
This is how my command looked like (don’t forget to press Enter after you typed the location where the Python script is stored on your computer):
Next, use the following template to create the executable:
pyinstaller --onefile pythonScriptName.py
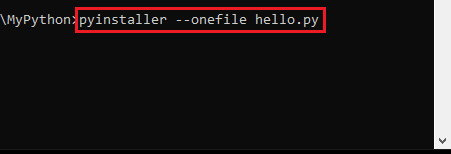
Since in our example, the pythonScriptName is ‘hello‘, then the command to create the executable is:
pyinstaller --onefile hello.py
In the command prompt:
Once you’re done, press Enter for the last time.
Step 6: Run the Executable
Your executable should now get created at the location that you specified.
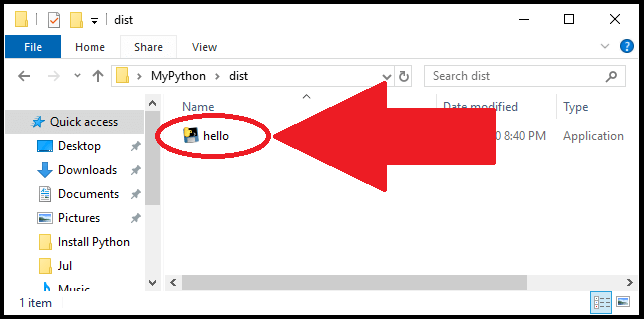
In my case, I went back to the location where I originally stored the ‘hello’ script (C:\Users\myTechMint\Desktop\MyPython). Few additional files got created at that location. To find the executable file, open the dist folder:
Now you’ll see the executable file:
Once you click on the file, you should be able to launch your program (if you get an error message, you may need to install Visual C++ Redistributable).
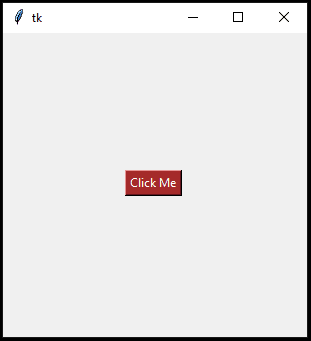
For our example, once you click on the ‘hello’ executable, you’ll see the following display with a single button:
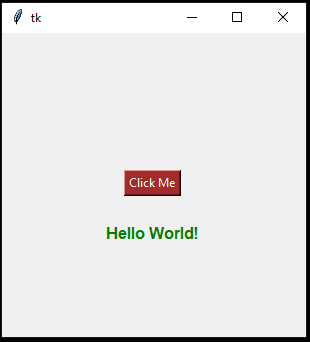
If you click on the button, you’ll see the expression of ‘Hello World!’
You can read more about pyinstaller by visiting the pyinstaller manual.